Here is my dataset for this example:
The first thing I want to do is look at my data overall - get the range of values for each variable, and see what missing values I have. I can do this simply by doing:
summary(mydata)
This produces the output below, and shows me that both Weight and Height have missing values. The Migrantstatus variable is a factor (categorical), so it lists the number in each category.
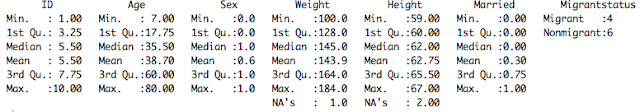
If I want to just summarize one variable, I can do summary(mydata$Weight) for example. And remember from last week, that if I just want to summarize some portion of my data, I can subset using indexing like so: summary(mydata[,c(2:5)])
Next, I want to tabulate my data. I can do univariate and bivariate tables (I can even do more dimensions than that!) by using the table() function. Table() gives me the totals in each group. If I want proportions instead of totals, I can use prop.table() around my table() function. The code looks like this with the output below:
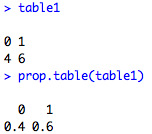
table1<-table(mydata$Sex)
table1
prop.table(table1)
Next, I do the bivariate tables. The first variable is the row and the second is the column. I can do proportions here as well, but I must be careful about the margin. Margin=1 means that R calculates the proportions across rows, while margin=2 is down columns. I show a table of Sex vs Marital status below with two types of proportion tables.
table2<-table(mydata$Sex, mydata$Married)
table2
prop.table(table2, margin=1)
prop.table(table2, margin=2)
table3<-table(mydata$Sex, mydata$Married, mydata$Migrantstatus)
The great part about R is that I can take any component of this table that I want. For example, if I just want the table for migrants, I can do:
table3[,,1]
which tells R to give me all rows and columns, but only for the first category of the third variable. I get the following output, which you can see is the same as the first part of table 3 from above.
Finally, what if I want to calculate the mean of one variable by another variable? One way to do this is to use the aggregate() function. Aggregate does exactly that: it takes one variable (the first argument) and calculates some kind of function on it (the FUN= argument), by another variable (the by=list() argument). So here I am going to do the mean weight for each sex. Here the syntax is a little funny because R wants a list for the by variable. I will go over lists at another post in the future, or you can look it up on another R site.
aggtable
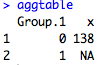
However, something is wrong. The NA in the weight column is messing up my mean calculation. To get around this, I use the na.rm=TRUE parameter which removes any NAs from consideration.
aggtable.narm<-aggregate(mydata$Weight, by=list(mydata$Sex), FUN=mean, na.rm=TRUE)
aggtable.narm
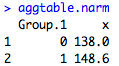
Victory! If I want to name my columns of this table, I can do:
names(aggtable.narm)<-c("Sex","Meanweight")
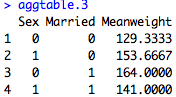
And of course if you want to do mean tables by more than one variable, you can put the all in the list argument, like so: by=list(mydata$Sex, mydata$Married). The code and output would look like this:
aggtable.3<-aggregate(mydata$Weight, by=list(mydata$Sex, mydata$Married), FUN=mean, na.rm=TRUE)
names(aggtable.3)<-c("Sex","Married","Meanweight")
aggtable.3




Keep it up!
ReplyDeleteYour post is very effective and good in different ways.This is really good site and I often visit your posts.Thanks for sharing such nice posts.Good work.
ReplyDeleteI love to summarize data in the form of the rows, in between the rows I have used the international business research paper topics to increase the value of the data that I have collected.
ReplyDelete